Boids algorithm - augmented for distributed consensus¶
V. Hunter Adams (vha3@cornell.edu)¶
HTML('''<script>
code_show=true;
function code_toggle() {
if (code_show){
$('div.input').hide();
} else {
$('div.input').show();
}
code_show = !code_show
}
$( document ).ready(code_toggle);
</script>
<form action="javascript:code_toggle()"><input type="submit" value="Click here to toggle on/off the raw code."></form>''')
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from IPython.display import Audio
from IPython.display import Image
from scipy import signal
from scipy.fft import fftshift
from scipy.io import wavfile
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [12, 3]
from IPython.core.display import HTML
HTML("""
<style>
.output_png {
display: table-cell;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: middle;
}
</style>
""")
Table of Contents¶
Background and Introduction¶
Boids is an artificial life program that produces startlingly realistic simulations of flocking behavior. Each "boid" (which is an abbreviation of "bird-oid object" follows a very simple set of rules. These rules will be discussed at length, but they can be summarized as follows:
- Separation: boids move away from other boids that are too close
- Alignment: boids attempt to match the velocities of their neighbors
- Cohesion: boids move toward the center of mass of their neighbors
We will add a few more rules to this list. In particular, boids will turn around at the boundaries of the VGA display, their speeds will be constrained to within a configurable range, and a subset of configurable size will be biased toward one side of the screen or the other. With the addition of these rules, we will be able to observe the decision-making processes described in Couzin et al's "Effective leadership and decision-making in animal groups on the move."
When all of the boids follow these simple rules, the flock produces gorgeously organic-looking emergent patterns, as shown in the video below. You can compare the behavior shown in the simulation below to videos of actual murmurations of starlings (like this one). These rules are also extendable. You might add a predator that all the boids must avoid, or you might add a "perching" behavior where boids near the bottom of the screen rest for a moment before rejoining the flock. The Boids algorithm was developed by Craig Reynolds in 1986.
Algorithm Overview¶
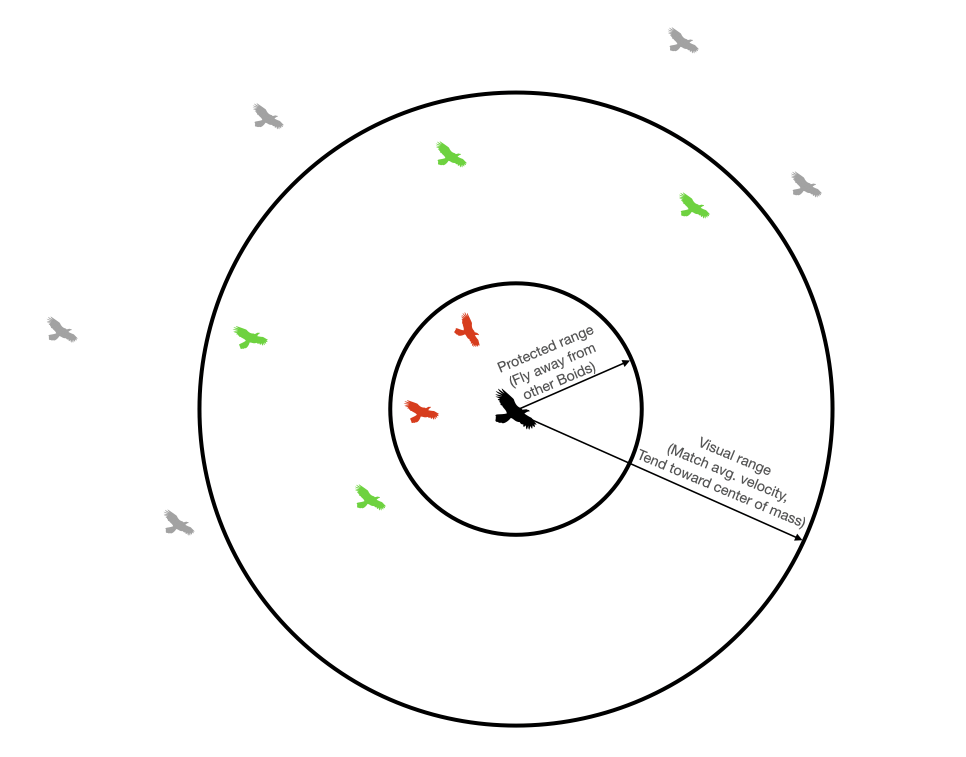
Just like in nature, no boid has global knowledge of every other boid in the flock. Instead, each can only see boids that are within its visual range and that are within its smaller protected range. These are tunable parameters. A boid will move away from other boids that are within its protected range (birds don't want to fly into each other), it will attempt to match the average velocity of boids within its visible range, and it will tend toward the center of mass of boids in its visible range.
We will also enforce minimum and maximum speed limits for the boids. Flocking birds (like starlings) are never stationary in flight. So, we'll prevent the speed of any boid from dropping below some tunable value. Birds also have maximum speeeds, so we'll prevent the speed of any boid from exceeding some tunable value. Finally, we want for the boids to turn around when they reach the edges of the TFT screen. When a boid gets within some tunable margin of an edge of the screen, we will turn it by some tunable value. The greater this value, the faster the birds will be able to turn. We can play with these parameters until we get realistic-looking behavior.
The state for each boid includes its x/y position and its x/y velocity, represented as:
boid.x
boid.y
boid.vx
boid.vy
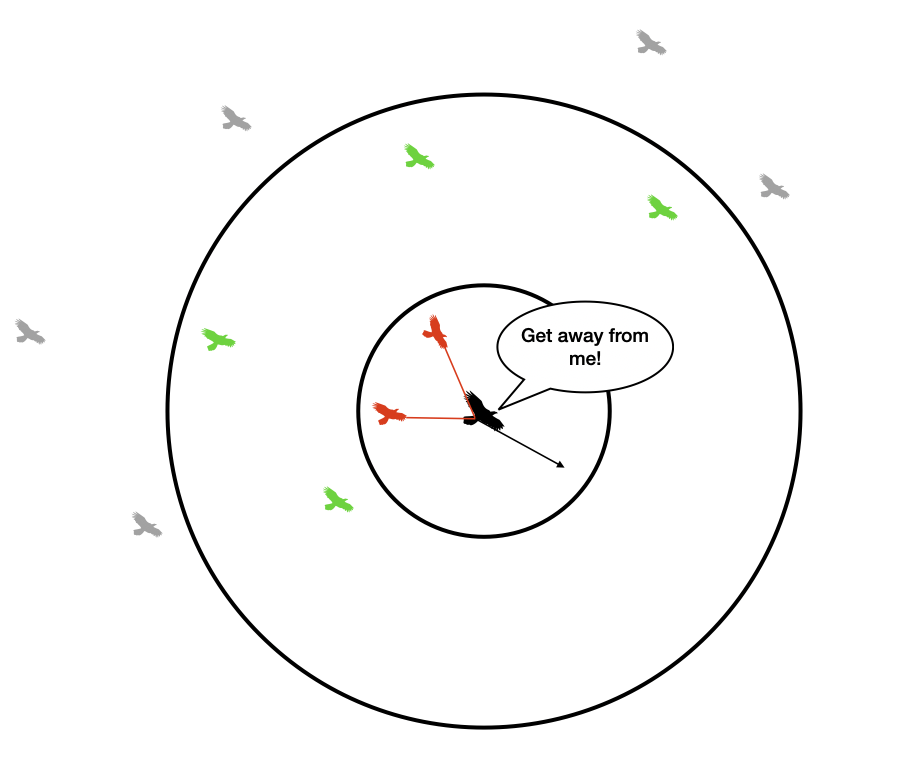
Separation¶
Each boid attempts to avoid running into other boids. If two or more boids get too close to one another (i.e. within one another's protected range), they will steer away from one another. They will do so in the following way:
- At the start of the update for a particular boid, two accumulating variable (
close_dxandclose_dy) are zeroed - We loop thru every other boid. If the distance to a particular boid is less than the protected range, then
close_dx += boid.x - otherboid.xclose_dy += boid.y - otherboid.y. - Once we've looped through all other boids, then we update the velocity according to
boid.vx += close_dx*avoidfactorboid.vy += close_dy*avoidfactor
(whereavoidfactoris a tunable parameter)
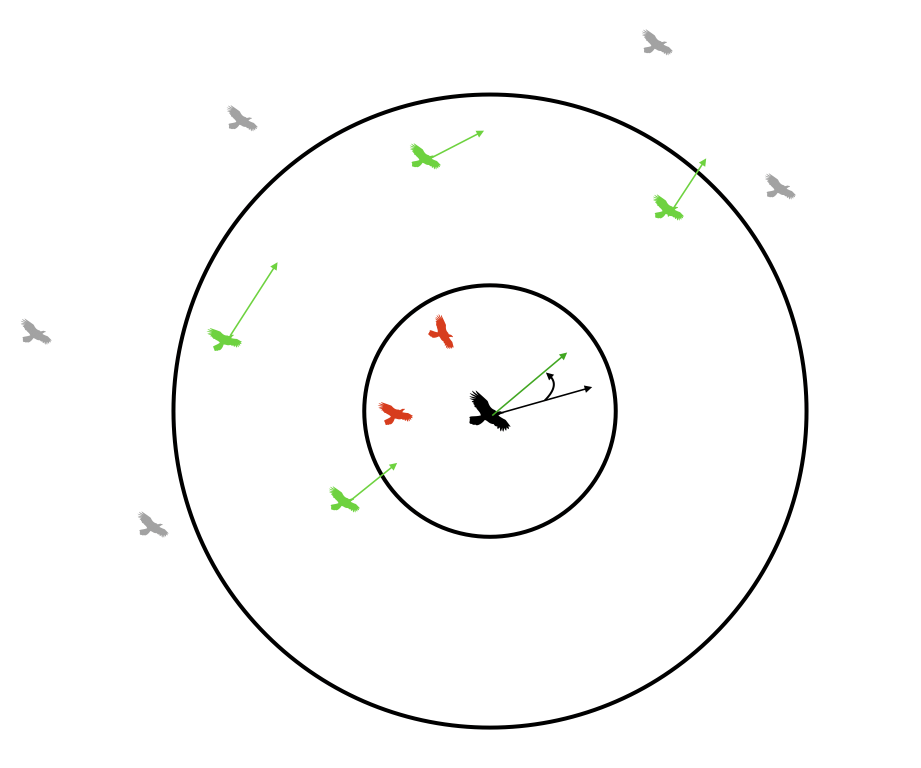
Alignment¶
Each boid attempts to match the velocity of other boids inside its visible range. It does so in the following way:
- At the start of the update for a particular boid, three variables (
xvel_avg,yvel_avg, andneighboring_boids) are zeroed - We loop thru every other boid. If the distance to a particular boid is less than the visible range, then
xvel_avg += otherboid.vx
yvel_avg += otherboid.vy
neighboring_boids += 1 - Once we've looped through all other boids, we do the following if
neighboring_boids>0:
xvel_avg = xvel_avg/neighboring_boids
yvel_avg = yvel_avg/neighboring_boids - We then update the velocity according to:
boid.vx += (xvel_avg - boid.vx)*matchingfactor
boid.vy += (yvel_avg - boid.vy)*matchingfactor
(wherematchingfactoris a tunable parameter)
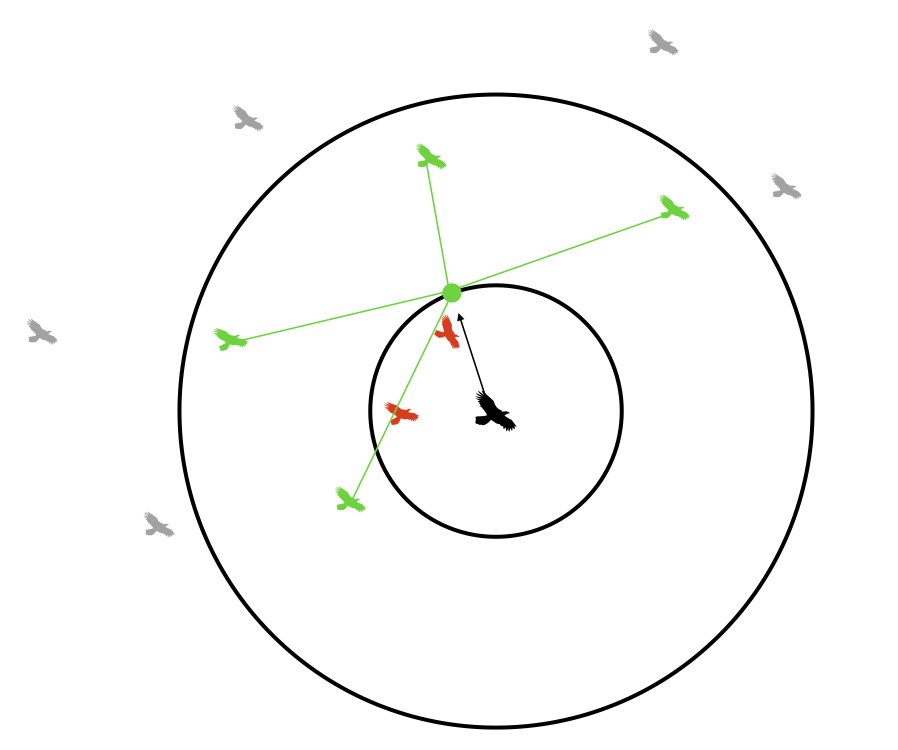
Cohesion¶
Each boid steers gently toward the center of mass of other boids within its visible range. It does so in the following way:
- At the start of the update for a particular boid, three variables (
xpos_avg,ypos_avg, andneighboring_boids) are zeroed - We loop thru every other boid. If the distance to a particular boid is less than the visible range, then
xpos_avg += otherboid.x
ypos_avg += otherboid.y
neighboring_boids += 1 - Once we've looped through all other boids, we do the following if
neighboring_boids>0:
xpos_avg = xpos_avg/neighboring_boids
ypos_avg = ypos_avg/neighboring_boids - We then update the velocity according to:
boid.vx += (xpos_avg - boid.x)*centeringfactor
boid.vy += (ypos_avg - boid.y)*centeringfactor
(wherecenteringfactoris a tunable parameter)
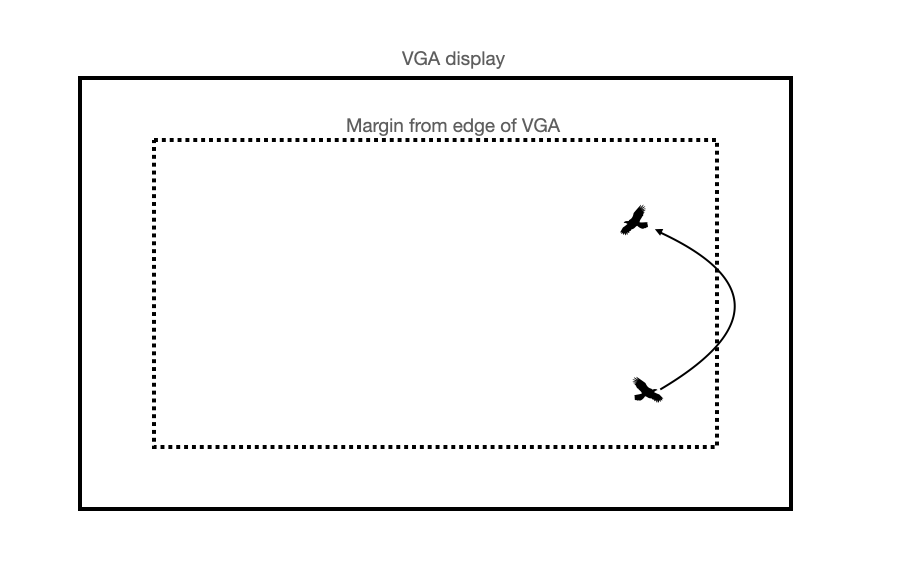
Screen edges¶
We want our boids to turn-around at an organic-looking turn radius when they approach an edge of the TFT. We will do so in the following way:
if boid.x < leftmargin:
boid.vx = boid.vx + turnfactor
if boid.x > rightmargin:
boid.vx = boid.vx - turnfactor
if boid.y > bottommargin:
boid.vy = boid.vy - turnfactor
if boid.y < topmargin:
boid.vy = boid.vy + turnfactorwhere turnfactor and all margins are tunable parameters. I recommend a margin of 100 pixels on all edges.
Bias¶
In accordance with Couzin's paper, we will allow for some boids to have a bias. This is to model a subset of the group that might know the direction of a food source, or have a preference toward a nest site. We will allow for two biased groups called scout group 1 and scout group 2. The first group will be biased to the right-side of the screen, and the second group will be biased toward the left side of the screen. The strength of their bias is determined by the magnitude of biasval. Their x-velocity is updated as a weighted average (weighted by biasval) between their unbiased velocity and their bias velocity.
# If the boid has a bias, bias it!
# biased to right of screen
if (boid in scout group 1):
boid.vx = (1 - boid.biasval)*boid.vx + (boid.biasval * 1)
# biased to left of screen
else if (boid in scout group 2):
boid.vx = (1 - boid.biasval)*boid.vx + (boid.biasval * (-1))
For 5730 students, biasval will be a dynamic variable. For 4760 students, this is a static (but user-specified) value.
Speed limits¶
We constrain the boids to move faster than some minimum speed and slower than some maximum speed. We do so in the following way:
- Once the velocity has been updated, compute the boid speed
speed = sqrt(boid.vx*boid.vx + boid.vy*boid.vy) - If
speed>maxspeed:
boid.vx = (boid.vx/speed)*maxspeed
boid.vy = (boid.vy/speed)*maxspeed - If
speed<minspeed:
boid.vx = (boid.vx/speed)*minspeed
boid.vy = (boid.vy/speed)*minspeed
Update position¶
With the updated velocity, we update the boid position. Assume that $\Delta t = 1$ from frame to frame (i.e. that velocity is in units of pixels/frame):
boid.x = boid.x + boid.vx
boid.y = boid.y + boid.vy
Recommended parameter values¶
You can play with these to get different emergent behaviors. These are the parameters that I used in the example videos on this webpage. Note that you will need to convert these to fixed-point.
turnfactor: 0.2
visualRange: 40
protectedRange: 8
centeringfactor: 0.0005
avoidfactor: 0.05
matchingfactor: 0.05
maxspeed: 6
minspeed: 3
maxbias: 0.01
bias_increment: 0.00004
default biasval: 0.001 (user-changeable, or updated dynamically)
Pseudocode¶
All of the above rules are represented in the below pseudocode. Look for places to optimize! This pseudocode describes the most straightforward implementation of the algorithm.
The user provides:
- number of boids in scout group 1
- number of boids in scout group 2
biasvalfor scout group 1biasvalfor scout group 2- (5730 only), dynamic updating for
biasvalenabled or disabled
Then, each frame is updated:
# For every boid . . .
for each boid (boid):
# Zero all accumulator variables (can't do this in one line in C)
xpos_avg, ypos_avg, xvel_avg, yvel_avg, neighboring_boids, close_dx, close_dy = 0
# For every other boid in the flock . . .
for each other boid (otherboid):
# Compute differences in x and y coordinates
dx = boid.x - otherboid.x
dy = boid.y - otherboid.y
# Are both those differences less than the visual range?
if (abs(dx)<visual_range and abs(dy)<visual_range):
# If so, calculate the squared distance
squared_distance = dx*dx + dy*dy
# Is squared distance less than the protected range?
if (squared_distance < protected_range_squared):
# If so, calculate difference in x/y-coordinates to nearfield boid
close_dx += boid.x - otherboid.x
close_dy += boid.y - otherboid.y
# If not in protected range, is the boid in the visual range?
else if (squared_distance < visual_range_squared):
# Add other boid's x/y-coord and x/y vel to accumulator variables
xpos_avg += otherboid.x
ypos_avg += otherboid.y
xvel_avg += otherboid.vx
yvel_avg += otherboid.vy
# Increment number of boids within visual range
neighboring_boids += 1
# If there were any boids in the visual range . . .
if (neighboring_boids > 0):
# Divide accumulator variables by number of boids in visual range
xpos_avg = xpos_avg/neighboring_boids
ypos_avg = ypos_avg/neighboring_boids
xvel_avg = xvel_avg/neighboring_boids
yvel_avg = yvel_avg/neighboring_boids
# Add the centering/matching contributions to velocity
boid.vx = (boid.vx +
(xpos_avg - boid.x)*centering_factor +
(xvel_avg - boid.vx)*matching_factor)
boid.vy = (boid.vy +
(ypos_avg - boid.y)*centering_factor +
(yvel_avg - boid.vy)*matching_factor)
# Add the avoidance contribution to velocity
boid.vx = boid.vx + (close_dx*avoidfactor)
boid.vy = boid.vy + (close_dy*avoidfactor)
# If the boid is near an edge, make it turn by turnfactor
# (this describes a box, will vary based on boundary conditions)
if outside top margin:
boid.vy = boid.vy + turnfactor
if outside right margin:
boid.vx = boid.vx - turnfactor
if outside left margin:
boid.vx = boid.vx + turnfactor
if outside bottom margin:
boid.vy = boid.vy - turnfactor
##############################################################
### ECE 5730 students only - dynamically update bias value ###
##############################################################
# biased to right of screen
if (boid in scout group 1):
if (boid.vx > 0):
boid.biasval = min(maxbias, boid.biasval + bias_increment)
else:
boid.biasval = max(bias_increment, boid.biasval - bias_increment)
# biased to left of screen
else if (boid in scout group 2): # biased to left of screen
if (boid.vx < 0):
boid.biasval = min(maxbias, boid.biasval + bias_increment)
else:
boid.biasval = max(bias_increment, boid.biasval - bias_increment)
##############################################################
# If the boid has a bias, bias it!
# biased to right of screen
if (boid in scout group 1):
boid.vx = (1 - boid.biasval)*boid.vx + (boid.biasval * 1)
# biased to left of screen
else if (boid in scout group 2):
boid.vx = (1 - boid.biasval)*boid.vx + (boid.biasval * (-1))
# Calculate the boid's speed
# Slow step! Lookup the "alpha max plus beta min" algorithm
speed = sqrt(boid.vx*boid.vx + boid.vy*boid.vy)
# Enforce min and max speeds
if speed < minspeed:
boid.vx = (boid.vx/speed)*minspeed
boid.vy = (boid.vy/speed)*minspeed
if speed > maxspeed:
boid.vx = (boid.vx/speed)*maxspeed
boid.vy = (boid.vy/speed)*maxspeed
# Update boid's position
boid.x = boid.x + boid.vx
boid.y = boid.y + boid.vy